Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine in women is a common occurrence after 40 years;Its development is caused by a combination of many factors (age, inactive lifestyle, load on the cervical spine).Under their influence, the elasticity and strength of the intervertebral discs are lost (degenerative-dystrophic changes), their elasticity and height are reduced.
At first, the symptoms of osteochondrosis may be almost invisible (muscle tension, skin numbness), then they increase, and the patient develops signs of cerebral circulation problems (headaches, impaired vision, hearing, memory, pressure surges).Such violations are dangerous - they can cause the development of:
- persistent hypertension (high blood pressure);
- hypertensive crisis (bleeding in brain tissue);
- Neurovascular pathology (decreased muscle strength to complete arm immobility).
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine in women and men begins and develops according to the same scenario;There is no specific difference in the cause, symptoms and treatment of the disease.Some experts note that women more often seek medical help during menopause: in 2/3 of patients, almost all chronic pathologies worsen at the time of hormonal changes, and cervical osteochondrosis is no exception.
Age-related changes in intervertebral disc tissue are irreversible, so it is impossible to completely eliminate pathology.In the early stages, its development can be stopped with special gymnastics and other physiotherapy procedures.After the appearance of intervertebral hernia, surgical restoration of vertebral height is recommended.
The treatment of cervical osteochondrosis has its own characteristics (related to the fragility and small size of the department's vertebrae), but it is almost no different from the treatment of thoracic or lumbar osteochondrosis.
At the first signs of this disease, consult a vertebrologist or orthopedist.Various manifestations of cervical osteochondrosis (sleep, vision, hearing, pressure changes) are treated by therapists and neurologists.
Overview of Symptoms
Signs of neck damage in women are almost invisible at first, so the early stages of the pathology are quite difficult to diagnose.The first to appear is tension, neck muscle fatigue and increased headaches.
As the disease progresses in women, the symptoms increase with severe pain in the neck, back of the head, shoulders, shoulder blades and a clear crisis when turning the head.
In the future, osteochondrosis in women manifests itself as impaired mobility (it is difficult to turn the head, this causes pain), weakness of the upper limbs (to the point of complete immobility), poor vision and many other symptoms.
Listed below are the most common pathological manifestations, starting with the most common:
- Painful muscle tension is a response to the "sinking" of the intervertebral disc, displacement of the vertebrae.The body tries to balance, align, maintain the spine in the correct position, because of this, muscle overstrain occurs, and subsequently their atrophy (weakness).
- Acute burning or tearing, squeezing pain in the back of the head, neck, shoulder, shoulder blade is the result of muscle spasm (tension), compression of blood vessels and nerve endings (for example, going to the occipital region of the head).The pain syndrome is not relieved by painkillers, can be intensified from a long time in a forced position, and radiates to the chest and arms.
- Cracking, crunching during movement and limited movement of the spine in the cervical region - occurs against the background of "sinking" of the intervertebral disc and the growth of the bone surface of the vertebral body.
- Affected skin sensitivity, weakness of the muscles of the upper limbs and fingers, and shoulder straps (to the point of complete immobility) is explained by the involvement in the pathological process of the nerve endings that provide communication between these organs and the spinal column.
- Smooth and strong tinnitus, dizziness, nausea (to the point of vomiting), coordination of movement movements, changes in blood pressure - the result of deformation (narrowing, compression) of the large vertebral artery, which provides blood delivery to the brain (to the cerebellum and occiput).
- The appearance of hiccups and lack of air (impossibility to fully "inhale") is caused by irritation of the phrenic nerve.

With advanced cervical osteochondrosis, symptoms may include:
- incorrect position, deviation of the head (torticollis);
- difficulty with swallowing (if the nerves of the pharynx and larynx are involved in the process);
- Sleep disturbances, mood swings, depression, panic attacks;
- weakness of attention, memory;
- rapid heartbeat.
Treatment methods
Pathology cannot be completely cured, because the changes that occur in the intervertebral disc cannot be restored.The treatment algorithm for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine in women is the same as in men.
The therapeutic approach is comprehensive:
- With the help of drug therapy, they eliminate severe manifestations of osteochondrosis (pain, tension);
- Physiotherapy improves the nutrition of the paravertebral tissue, restores the mobility of the spine;
- Therapeutic exercises strengthen the muscles, "stretch" the spine, reduce the load on the disc (in the stage of stable remission or asymptomatic course).
It is recommended to do gymnastics constantly (throughout your life), this will help stop the final deformation of the vertebrae and the development of all kinds of complications.
Drug therapy
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis in women is carried out using conservative methods;Symptoms of the disease (pain, cerebral circulation disorders, sensitivity) are relieved with medicines.
| Drug group | What is it prescribed for? |
|---|---|
Non-hormonal pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs |
Reduces inflammation and pain |
Angioprotectors |
Improves blood circulation, promotes tissue oxygen saturation |
Muscle relaxants |
Relaxes the muscles in the cervical area, improves blood circulation |
B vitamins |
Stimulates the rapid recovery of nerve tissue, increases the effect of anti-inflammatory and painkillers, improves metabolism |
Chondroprotectors |
With long-term use, the destruction of cartilage tissue is stopped |
In case of severe pain in the pinched nerve area, analgesic, anti-inflammatory blocks are given in the paravertebral muscles.The neck is immobilized using a special orthopedic collar or splint shants (it reduces the load on the muscles of the collar area).
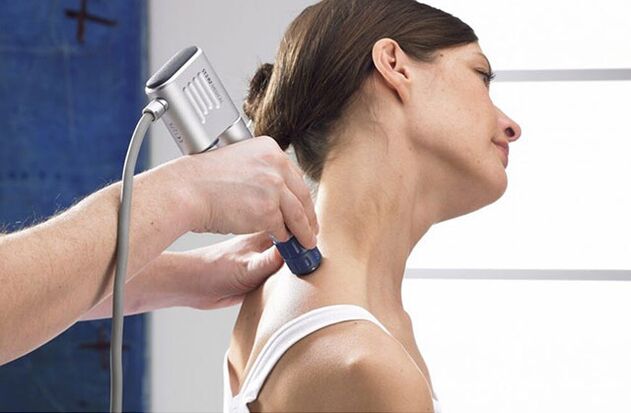
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy treatment gives good results for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine:
| Method | What function do they perform? |
|---|---|
Magnetotherapy |
Stimulates blood circulation, relieves swelling and pain |
Ultrasound |
Stimulates local blood circulation, improves tissue healing |
Electrophoresis with drugs |
Provides drug delivery through the skin barrier to the source of pain, quickly relieves pronounced and residual signs of cervical osteochondrosis |
Therapeutic massage of the collar area |
Relaxes muscles, improves blood circulation, stimulates tissue oxygen saturation |
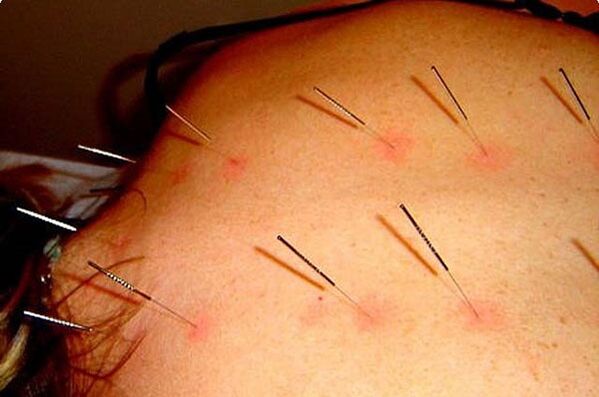
Acupuncture |
Stimulates biologically active points in the body, quickly relieving the residual symptoms of the disease |
Women with cervical osteochondrosis benefit from:
- Sanatorium-resort treatment in a specialized sanatorium (up to 2 times a year).
- Mud therapy.
- Application of heating (paraffin therapy).
- Balneotherapy (therapeutic bath).
Patients are absolutely not recommended to overcool (especially after physiotherapy).
Gymnastics for cervical osteochondrosis
Physical therapy exercises can stop the progress of osteochondrosis.They are performed to relieve muscle tension, strengthen the muscles and ligaments of the cervical spine, and relieve pressure on the vertebrae.
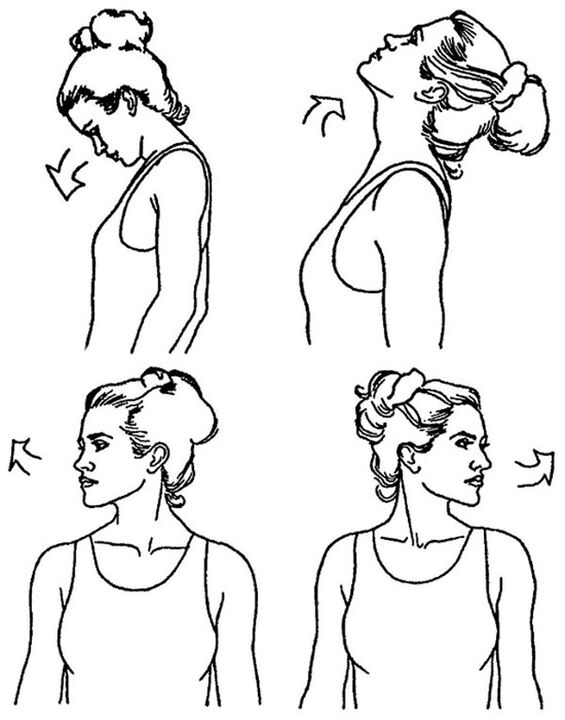
Basic exercises for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are performed sitting or standing, smoothly, without jerking or straining (2-3 minutes daily):
- Tilt your head left and right (towards your shoulders).
- Tilt your head forward (touch your chin to your chest) and then back (touch the back of your head).
- Turn your head to the right (look over your right shoulder) and to the left (look over your left shoulder).
- Lower your head down, touching your chin to your chest.Turn left and right from shoulder to shoulder and back (as if "rolling" your head over your chest).
- Move your head back, turn left and right and back ("roll" behind you from shoulder to shoulder).
- Make a full circular rotation with your head from left to right, and then from right to left.
- Raise your shoulders (at the same time), lower them.
- Move your shoulders forward and then back.
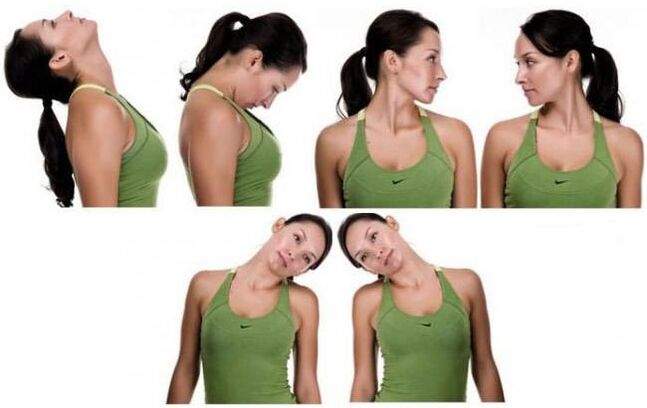

Gymnastics is performed during a period of stable remission (when there are no manifestations of the disease - pain, swelling, inflammation).
If, during exercise, any unpleasant signs of cervical osteochondrosis occur in women ("floaters" before the eyes, nausea, dizziness), take a break from exercise.If the sensation persists, you should consult your physiotherapist or doctor.
Nutrition for cervical osteochondrosis
With osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, you can adhere to the general principles of a healthy diet, observing the basic rules - food should be complete and varied:
- You need to introduce food into your diet - a source of amino acids, vitamins, minerals that participate in the synthesis of collagen, glycosaminoglycans (important for cartilage), improve metabolism, and stimulate the rapid recovery of damaged tissue.
- Limit the use of alcohol, strong tea and coffee, salty, smoked and fried foods.This product irritates the inflamed tissue and increases the pain.
What products are recommended for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine:
| Ingredients needed in the composition | Product list |
|---|---|
Natural glycosaminoglycans |
Chicken, beef, red fish, hard cheese, avocado, soy, products with gelatin |
Vitamins E and A |
Eggs, liver, fish, vegetable oils, nuts, seeds |
Vitamin c |
Citrus fruits, berries, vegetables |
B vitamins |
Lean meat, seafood, nuts, grains, cheese, milk |
Vitamin d |
Sea fish, sea fish liver, butter, raw egg yolk |
Vitamin pp |
Vegetables, grains, sea fish, beans |
Calcium |
Cottage cheese, cheese, milk, fermented milk products |
Magnesium |
Dark chocolate, rice bran, beans, grains |
Phosphorus |
Sea fish, seafood, legumes, milk, hard cheese |
Sulphur |
Nuts, chicken, hard cheese, beans |
Potassium |
Nuts, beans, prunes, bananas, garlic |
To maintain a normal body weight, it is recommended to limit the consumption of fast carbohydrates (sugar, sweets, sugar), fatty meat, lard, and margarine.















































